Understanding the Prostate and Its Functions
The prostate gland plays a crucial role in male reproductive health, serving as a key player in the production of seminal fluid, which is essential for fertility. Understanding what the prostate does in a man helps highlight its importance in ensuring healthy reproductive function.
Anatomy of the Prostate
Location and Size
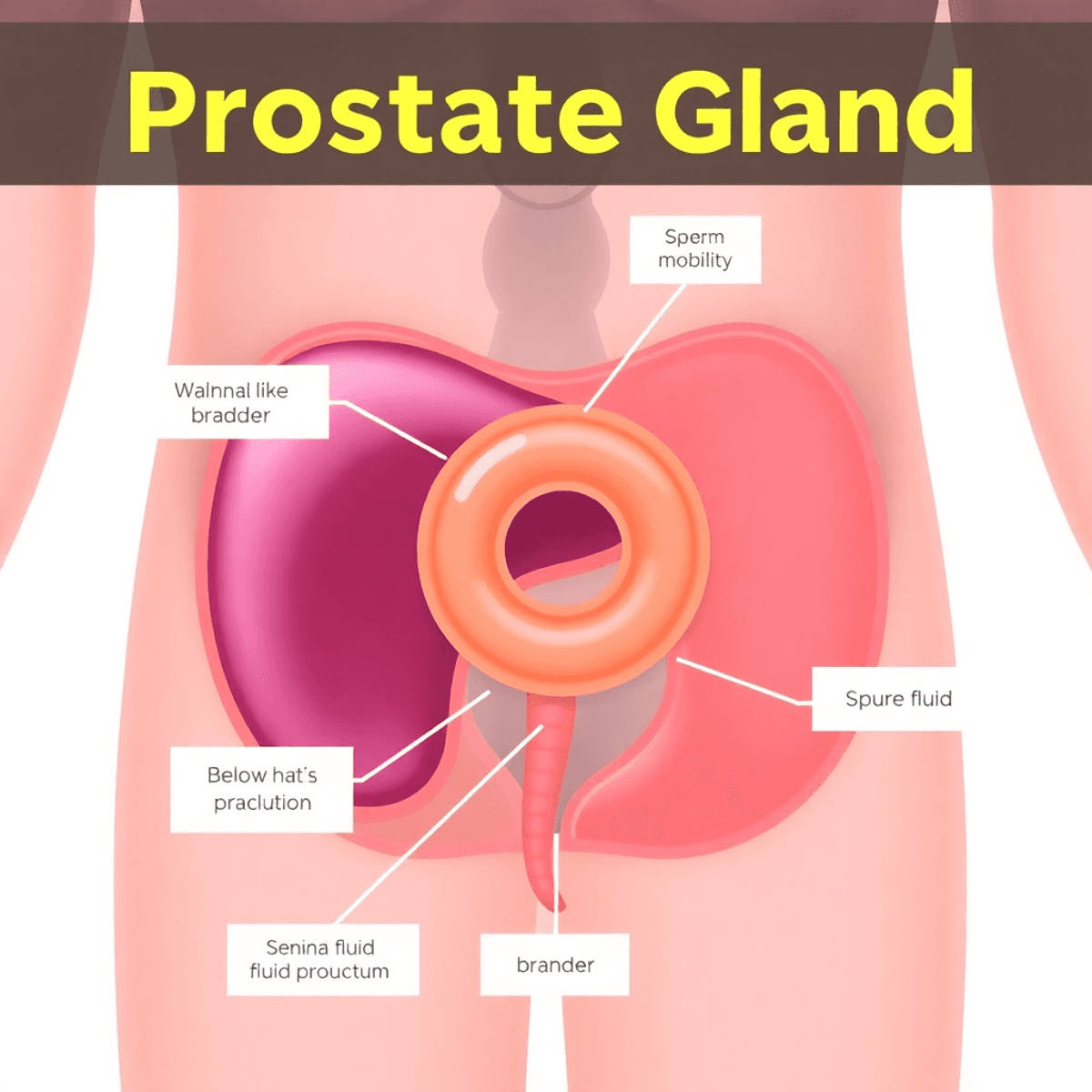
The prostate is positioned just below the bladder and in front of the rectum. It surrounds the urethra, forming an integral part of the male urinary and reproductive systems. Anatomically, it is often compared to the size of a walnut, providing a useful visualisation due to its small yet significant presence.
Shape
Its shape resembles that of a donut with a hole through which the urethra passes. This positioning allows it to exert influence on both urinary and sexual functions.
Role in Semen Production
The prostate’s primary function revolves around semen production:
- Seminal Fluid Production: The prostate produces a substantial portion of the seminal fluid. This fluid plays several essential roles:
- Nourishment: It provides nutrients that sustain sperm cells.
- Transport: Seminal fluid facilitates the movement of sperm through the male reproductive tract during ejaculation.
- Overall Fertility: By aiding sperm mobility and protecting them within the female reproductive system, the seminal fluid enhances overall fertility potential.
Importance of Prostate Function
Understanding prostate function underscores its significance beyond merely producing fluids:
- Sperm Mobility: The components secreted by the prostate ensure that sperm remain viable and mobile after ejaculation, increasing their chances of successful fertilisation.
- Reproductive Health: Any dysfunction or disease affecting the prostate can have direct implications on male fertility, making prostate health monitoring crucial. For instance, an enlarged prostate can lead to various complications; hence understanding how to shrink an enlarged prostate is essential for maintaining reproductive health.
Recognising these aspects provides insight into why maintaining optimal prostate health is vital for men.
The Role of Prostate Fluid in Male Reproductive Health
The prostate gland is essential for male reproductive health as it produces various substances necessary for fertility. One of the main components of prostate fluid is prostate-specific antigen (PSA), an enzyme that helps liquefy semen and improve sperm mobility. By keeping semen at the right consistency, PSA ensures efficient sperm transport, which is crucial for successful fertilisation.
What Does Prostate Fluid Contain?
In addition to PSA, prostate fluid has several other components that work together to support sperm survival and movement:
- Alkaline substances: These help neutralise the acidity of the vaginal tract, making it easier for sperm to reach their destination.
- Nutrients: Prostate fluid contains various nutrients that nourish sperm cells during their journey.
How Does Prostate Fluid Interact with Other Glands?
Prostate fluid doesn’t function in isolation; it interacts closely with fluids from other reproductive glands, particularly the seminal vesicles. The seminal vesicles produce a significant portion of total seminal fluid volume, which is rich in fructose and other nutrients that provide energy for sperm cells.
Why Is This Interaction Important?
The combination of fluids from the prostate and seminal vesicles ensures that sperm are not only mobile but also well-nourished throughout their journey. This intricate balance between these fluids highlights the importance of each component in achieving reproductive success.
The Significance of Understanding These Interactions
By studying how PSA and other secretions contribute to semen consistency and function, researchers gain valuable insights into male fertility. This knowledge can potentially lead to therapeutic interventions when fertility issues arise.
Maintaining prostate health is vital for overall reproductive wellness, as it directly impacts the quality of prostate fluid produced.
Hormonal Regulation of Prostate Health
Male hormones are crucial for the development and function of the prostate. Two important hormones, testosterone and dihydrotestosterone (DHT), play a key role in this process.
The Role of Testosterone
Testosterone, mainly produced in the testicles, is the primary male hormone responsible for developing male traits and reproductive functions. It influences the growth and maintenance of the prostate gland by converting into its more powerful form, DHT.
The Role of Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is derived from testosterone through the action of an enzyme called 5-alpha-reductase. DHT binds to androgen receptors in prostate cells, driving tissue growth and function. This interaction ensures the prostate remains active in its role within male reproductive health.
Aging and Hormonal Changes
As men age, hormone levels change, which can affect prostate health. Testosterone levels naturally decrease with age, while DHT may still have a significant impact on the prostate. This hormonal shift is linked to conditions like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), where an enlarged prostate can cause urinary problems due to pressure on the urethra.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
BPH, often associated with aging, results from increased cell growth within the prostate that is partly driven by hormonal changes. The imbalance between declining testosterone and sustained DHT activity can contribute to this non-cancerous enlargement.
Prostate Cancer
Hormonal regulation also plays a role in developing prostate cancer. While not solely dependent on hormones, elevated levels of testosterone and DHT can promote cancerous cell growth within the gland. Monitoring hormone levels becomes essential as men age to mitigate these risks.
Understanding these hormonal dynamics offers valuable insights into maintaining prostate health, especially as men get older. Recognising how testosterone and DHT affect the prostate can help guide proactive approaches to managing potential health issues.
The Prostate’s Role in Sexual Functioning
Understanding what does a prostate do in a man extends to its critical role in sexual functioning. The prostate gland contributes significantly to the male reproductive system through its involvement in sexual arousal and ejaculation.
Muscle Contractions and Sexual Arousal
During sexual arousal, the prostate is not just a passive participant. It actively engages through muscle contractions. These contractions are part of a complex series of events that prepare the body for ejaculation:
- Prostatic muscles: These muscles are smooth and involuntary, meaning they respond automatically during sexual stimulation.
- Contraction mechanism: When aroused, these muscles contract rhythmically, helping propel prostatic fluid along with sperm from the testicles into the urethra.
This orchestrated activity ensures that seminal fluid is mixed thoroughly with sperm, enhancing mobility and viability.
Ejaculation Mechanism
The act of ejaculation is where the prostate’s role becomes most evident. It assists in expelling semen from the body by:
- Pressure generation: The rhythmic contractions create pressure that drives the fluid forward.
- Fluid propulsion: Prostate fluid, enriched with enzymes like PSA, aids in making semen less viscous, facilitating easier passage through the urethra.
This process is crucial for effective semen expulsion, which ultimately supports reproduction by delivering sperm into the female reproductive tract. For those seeking to enhance their control over this process, exploring techniques such as Ejaculation By Command could be beneficial.
The prostate’s contribution to ejaculation underscores its importance beyond mere sperm transport. It’s an active participant in ensuring reproductive success, demonstrating why maintaining prostate health is vital for overall male sexual well-being. Understanding these functions highlights not just what does a prostate do in a man, but how integral it is to male vitality and fertility.
Common Prostate Health Issues and Their Impact on Men’s Well-being
Understanding common prostate health issues is crucial for maintaining overall male health. Here, we explore three primary concerns: benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), prostate cancer, and prostatitis.
Benign Prostatic Hyperplasia (BPH)
Symptoms:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream or a stream that stops and starts
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
Implications for Men’s Health:
BPH is a condition where the prostate gland enlarges with age. While it is non-cancerous, an enlarged prostate can press against the urethra, causing urinary symptoms that impact daily life and sleep quality. Left untreated, BPH can lead to bladder or kidney damage.
Understanding Prostate Cancer
Prostate cancer is a significant concern as it is one of the most common cancers among men.
Risk Factors:
- Age: Most cases occur in men over 50.
- Family History: A family history of prostate cancer increases risk.
- Race: African American men are more likely to develop prostate cancer.
Symptoms: Often asymptomatic in early stages but can include:
- Trouble urinating
- Blood in urine or semen
- Erectile dysfunction
Regular screenings are essential for early detection and effective management.
Prostatitis
Different from BPH and prostate cancer, prostatitis involves inflammation of the prostate gland.
Causes:
- Bacterial infection (acute bacterial prostatitis)
- Chronic non-bacterial factors (chronic pelvic pain syndrome)
Symptoms:
- Painful urination
- Groin pain
- Flu-like symptoms in acute cases
Available Treatments:
Treatment varies based on type:
- Antibiotics for bacterial infections
- Alpha-blockers to relax muscle fibres within the prostate for symptom relief
- Anti-inflammatory medications for pain management
Addressing these common issues through awareness and proactive health management can significantly enhance quality of life. Regular medical check-ups and lifestyle adjustments are key strategies in managing these conditions effectively.
Age-Related Changes in Prostate Function and Health Maintenance Strategies
Understanding Aging Effects on the Prostate
As men age, changes in prostate function are common. The prostate, essential for reproductive health, can undergo transformations that may affect overall well-being. These changes often manifest as benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH), where the prostate enlarges and can lead to symptoms such as:
- Frequent urination, especially at night
- Difficulty starting urination
- Weak urine stream or a stream that stops and starts
- Inability to completely empty the bladder
Such symptoms highlight the importance of understanding what does a prostate do in a man and how aging influences its functionality. Addressing these concerns through a proactive approach can mitigate discomfort and improve quality of life.
Lifestyle Choices for a Healthy Prostate
Dietary Recommendations:
A balanced diet plays a crucial role in maintaining a healthy prostate. Including specific foods can support prostate health by providing essential nutrients and antioxidants. However, it’s equally important to avoid certain foods that could harm prostate health. For comprehensive dietary guidance, refer to this comprehensive guide to prostate health, which includes recommendations on what to eat and what to avoid.
- Fruits and Vegetables: Rich in vitamins, minerals, and antioxidants, fruits like tomatoes (high in lycopene) and vegetables such as broccoli provide protective benefits.
- Healthy Fats: Incorporating healthy fats from sources like olive oil, nuts, and fatty fish (rich in omega-3 fatty acids) can support hormone regulation and reduce inflammation.
Maintaining a diet focused on whole foods not only benefits prostate health but also contributes to overall wellness.
Physical Activity:
Regular exercise is another cornerstone of promoting male health. Physical activity can help manage weight, improve cardiovascular health, and enhance mood—all factors that indirectly support the prostate.
- Aerobic Exercise: Activities such as walking, jogging, or swimming improve blood circulation and metabolic functions.
- Strength Training: Building muscle mass through resistance exercises aids hormone balance and supports a strong skeletal structure.
Engaging in consistent physical activity ensures that you remain physically fit while guarding against age-related complications.
Hydration:
Staying adequately hydrated is often overlooked but critical for optimal prostate function. Proper hydration supports urinary tract health and prevents conditions like urinary tract infections (UTIs), which can exacerbate prostate issues.
- Aim for at least 8 cups of water daily
- Adjust intake based on activity level, climate, and individual needs
By prioritising hydration, you contribute significantly to maintaining a healthy urinary system.
Embracing Change with Knowledge
Awareness of how aging affects the prostate empowers individuals to make informed decisions about their health journey. Through conscious lifestyle choices—balanced diet based on The Prostate Protocol, regular exercise, and proper hydration—you maintain not only your prostate health but also your overall vitality. Recognising the signs of an enlarged prostate early enables timely intervention and management strategies tailored to personal needs.
Proactive Measures: Regular Screening and Early Detection Methods
Understanding how aging affects the prostate is crucial for early detection and prevention of potential health issues like benign prostatic hyperplasia (BPH) or prostate cancer. As men age, changes in prostate size and function can lead to symptoms such as urinary difficulties due to an enlarged prostate. Identifying these changes early through regular screenings can significantly improve management and outcomes.
Screening Methods:
- Prostate-Specific Antigen (PSA) Testing: A blood test measuring the level of PSA in the blood. Elevated levels may indicate an enlarged prostate, infection, or cancer. While not definitive, it’s a valuable tool for assessing prostate health.
- Digital Rectal Exam (DRE): A physical examination where a healthcare provider checks the size and shape of the prostate by inserting a gloved finger into the rectum. DRE can help detect abnormalities that might require further investigation.
Recommended Age for Screenings:
It is generally advised to start regular screenings around age 50. However, those with a family history of prostate issues or African American men may need to begin earlier, potentially around age 45. The frequency of these screenings should be discussed with your healthcare provider based on individual risk factors and overall lifestyle choices for prostate health.
Regular screenings are vital in managing the changes that occur in the prostate as men age. Early detection through PSA testing and DRE can be instrumental in addressing issues before they develop into more serious conditions.
Taking Charge of Your Prostate Health Journey
Being proactive about your prostate health can greatly improve your overall well-being. Here are some healthy lifestyle choices you should prioritise:
- Balanced diet: Incorporate fruits, vegetables, and healthy fats into your meals.
- Regular physical activity: Engage in exercises that promote overall male health.
- Staying hydrated: Ensure optimal prostate function through adequate water intake.
The Importance of Regular Screenings
Regular screenings are crucial for maintaining prostate health. They allow for the early detection of conditions like BPH or prostate cancer, which can be pivotal in managing these issues effectively. It’s important to seek medical advice when symptoms arise.
Additional Resources for Optimal Health
If you’re looking for more guidance on maintaining optimal health, TC24 offers valuable resources. Understanding “What Does a Prostate Do in a Man” is just the beginning. Taking charge of your prostate health today helps ensure vitality for the future.

Leave a Reply