Introduction
Free electricity isn’t just a fantasy; it’s something many people can actually achieve. By producing your own energy, you can use nature’s endless resources to power your home or business. This change isn’t only about cutting costs—it’s also about taking advantage of the many benefits of renewable energy that are accessible today.
Why Generate Your Own Electricity?
Here are some reasons why generating your own electricity is beneficial:
- Energy Independence: When you make your own electricity, you rely less on traditional energy providers. This independence can protect you from rising energy costs and supply disruptions.
- Eco-Friendly Options: The environment offers several ways to generate free electricity, such as solar power, wind power, hydroelectricity, biomass energy, and ground source heat pumps. Each method uses different natural elements to create sustainable energy.
- Sustainable Living: Adopting renewable technologies is a step towards a more sustainable lifestyle. By reducing reliance on fossil fuels, you contribute positively to environmental conservation efforts.
- Financial and Global Benefits: Whether you’re motivated by saving money or caring for the planet, generating your own power brings advantages both personally and globally.
The journey towards self-sufficiency doesn’t stop with free electricity generation. The concepts behind manifestation can also be applied to other aspects of life. Embracing these strategies can further enhance your financial independence and overall lifestyle.
Understanding Free Electricity
What is Free Electricity?
Free electricity refers to the generation of power without ongoing costs, primarily through renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectricity, biomass, and ground source heat pumps. This approach leverages naturally occurring elements to produce energy, reducing or eliminating the need for traditional utility reliance.
Financial and Environmental Benefits
Generating your own power offers several advantages:
- Cost Savings: By investing in renewable systems, you can significantly lower or even eliminate monthly energy bills. The initial setup can be offset by long-term savings. This transition not only fosters financial freedom but also champions environmental responsibility.
- Energy Independence: Producing your own electricity reduces dependence on external suppliers and fluctuating energy prices.
- Environmental Impact: Renewable energy systems reduce carbon footprints by decreasing reliance on fossil fuels. This shift contributes to a cleaner, more sustainable environment.
“The transition to free electricity not only fosters financial freedom but also champions environmental responsibility.”
Reducing Reliance on Fossil Fuels
Fossil fuels are a major cause of pollution and climate change. Embracing free electricity helps minimise this dependency. Renewable energy sources are abundant and sustainable, offering a viable pathway to decarbonise power consumption. By choosing renewables, you’re supporting a future where clean energy is accessible to all.
If you’re interested in learning how to start generating your own electricity, check out this beginner’s guide.
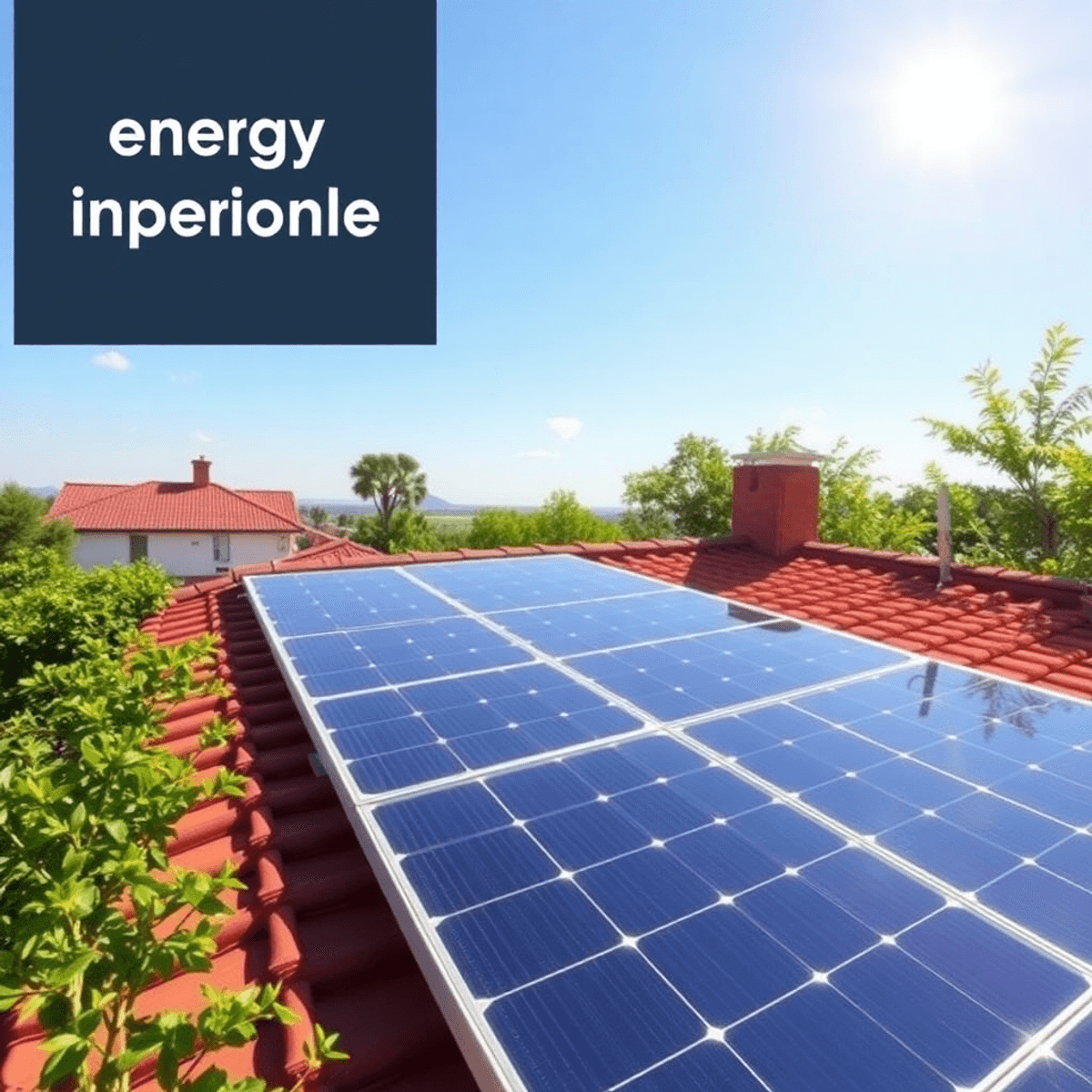
Step 1: Harnessing Solar Power
Embracing solar energy is a crucial step in achieving free electricity. With advancements in photovoltaic technology, more homeowners are considering residential solar options to tap into this clean and renewable energy source. This section delves into the intricacies of choosing the right solar system for your home, ensuring that you can make informed decisions about your investment.
Choosing the Right Solar System for Your Home
Selecting an appropriate solar system involves various factors that can significantly impact its efficiency and suitability for your specific needs. Here’s what you need to consider:
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Solar System
- Size: The size of the solar system is crucial as it determines how much electricity it can generate. A larger system typically means more panels, which translates into higher energy output. However, it also requires more space on your roof or property.
- Efficiency: Efficiency refers to how well the panels convert sunlight into electricity. Higher efficiency panels might be more expensive but can produce more power in a limited space. Consider your roof area and budget when evaluating different options.
- Budget and Financing Options: While initial costs can be significant, many financing options are available, including loans, leases, and power purchase agreements (PPAs). These can make solar installations more accessible by reducing upfront expenses.
- Local Climate and Sunlight Exposure: Assess your local weather conditions and average sunlight exposure throughout the year. Areas with more sunny days will benefit more from solar systems.
- Installation Complexity: Some systems may require complex installations due to roof shape or angle. This could affect installation time and cost.
Overview of Popular Solar Panel Brands and Technologies
Numerous brands offer diverse technologies tailored for residential use:
- SunPower: Known for producing some of the highest efficiency panels on the market, SunPower’s Maxeon series offers a robust warranty and long-term performance guarantees.
- LG Solar: LG’s NeON series provides excellent efficiency and durability. They are popular for their sleek design and performance in low-light conditions.
- Panasonic: With HIT technology, Panasonic offers high-efficiency panels that perform well even under high temperatures, ensuring consistent energy generation.
- Canadian Solar: Offering a balance between cost and performance, Canadian Solar’s products are ideal for those seeking reliability without breaking the bank.
- Tesla Solar Roof: For those interested in integrating solar technology seamlessly into their home’s design, Tesla’s Solar Roof combines aesthetics with functionality.
Each brand brings unique strengths to the table; selecting one depends on your specific needs and priorities.
Harnessing solar power not only helps reduce electricity bills but also contributes positively to environmental sustainability efforts by decreasing dependence on fossil fuels. As you explore these options, keep these considerations in mind to ensure that you choose a system that aligns perfectly with your energy goals.
Solar Panel Installation: DIY or Professional?
Solar energy generation is an increasingly popular choice for those seeking free electricity through residential solar options. Understanding the installation process for solar panels is crucial when deciding between a DIY approach or hiring professionals.
Installation Process Overview
- Site Assessment: Determine the best location for your solar panels, typically a roof with unobstructed sunlight exposure.
- System Design: Select between grid-tied or off-grid systems based on your energy needs and local regulations.
- Mounting and Wiring: Install mounting hardware to secure the panels, then connect photovoltaic cells to the inverter using appropriate wiring.
- Inverter Connection: This device converts the DC power generated by the panels into AC power for home use.
- System Testing: Ensure all components function correctly and that the system is efficiently generating solar energy.
DIY Installation Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Cost Savings: Avoid professional labor fees, potentially reducing overall expenses.
- Learning Experience: Gain valuable knowledge about solar panel systems and their workings.
Cons:
- Complexity: Requires technical skills and understanding of electrical systems.
- Safety Risks: Potential hazards during installation, especially on rooftops.
Professional Installation Pros and Cons
Pros:
- Expertise: Professionals ensure optimal placement and system efficiency.
- Warranty Compliance: Many manufacturers require professional installation to validate warranties.
Cons:
- Higher Costs: Professional services add to initial investment costs.
- Scheduling: Coordination with installers may take time.
Choosing between DIY or professional installation depends on your budget, technical skills, and comfort level with handling electrical work. While DIY can lead to cost savings, professional installation provides peace of mind and ensures compliance with local regulations. Both methods promise potential savings on electricity bills as you harness free electricity through solar energy generation.
Step 2: Utilising Wind Power for Free Electricity Generation
Assessing Your Location’s Wind Energy Potential
Wind power generation offers a compelling option for free electricity in areas with adequate wind exposure. Before investing in small-scale wind energy, conducting a thorough wind site assessment is crucial. This process helps determine the feasibility and potential productivity of installing wind turbines on your property.
How to Assess Your Location for Wind Energy Potential
- Evaluate Average Wind Speed: Not all locations are suitable for wind power generation. Ideal sites typically have an average annual wind speed above 5 meters per second (m/s). Lower speeds may result in insufficient energy production to justify the investment.
- Observe Local Topography: The landscape plays a significant role in wind patterns. Open fields, hilltops, and coastal areas generally offer better conditions than densely populated or heavily wooded areas. Consider how nearby structures and natural features might block or redirect wind flow.
- Consider Seasonal Variations: Wind speeds can vary significantly throughout the year. An area with high winds during one season but low winds in others might not produce consistent power output.
- Check Zoning Regulations: Local regulations may restrict the installation of wind turbines due to noise, height limitations, or aesthetic concerns. Research any legal constraints in your area before proceeding.
- Assess Site Accessibility: Ensure that the chosen site can be easily accessed for installation and maintenance purposes. A remote or difficult-to-reach location can increase costs and complicate upkeep.
Tools and Resources for Measuring Wind Speed and Consistency
For an accurate assessment of your property’s potential for small-scale wind energy, leverage available tools and resources:
- Anemometers: These devices measure wind speed at various heights and are essential for obtaining reliable data about local conditions. Install anemometers at the proposed turbine height to gather precise readings over time.
- Wind Maps: Use online resources like the Global Wind Atlas or national databases to access general wind speed data for your region. While these maps provide a useful starting point, they should be supplemented with on-site measurements.
- Wind Measurement Services: Some companies offer professional wind measurement services, collecting data over several months using advanced equipment such as meteorological towers or remote sensing devices. This option provides comprehensive insights into both speed and direction patterns.
- Software Tools: Various software applications model potential energy output based on gathered data, topography, and turbine specifications. Programs like AWS Truepower’s Openwind help estimate productivity given specific site characteristics.
Understanding your location’s wind energy potential is the first step toward harnessing this renewable resource effectively. By thoroughly assessing these factors with appropriate tools, you set the foundation for successful wind power generation that contributes to achieving free electricity sustainably.
However, while you’re on this journey towards sustainability with renewable energy sources like wind power, it’s also crucial to consider other aspects of your lifestyle that could contribute to overall sustainability and health. For instance, incorporating fat-burning foods into your diet can help improve your metabolism and promote a healthier lifestyle, complementing your efforts in utilising renewable energy sources effectively.
Installing and Maintaining a Small Wind Turbine System
Introduction to Small-Scale Wind Turbines
Small-scale wind turbines offer an accessible way to harness wind power generation for free electricity. These systems are designed for residential or small business use, providing an eco-friendly alternative to traditional energy sources.
Ideal Locations for Wind Turbine Installation
Before installing wind turbines, assessing the wind energy potential of your location is crucial. Ideal sites are typically open areas with consistent wind flow:
- Rural Areas: Farmland or countryside settings often have fewer obstacles that can block wind.
- Coastal Regions: Breezy coastal zones are perfect for capturing wind energy.
- High Elevations: Elevated locations benefit from stronger and more reliable wind currents.
Types of Domestic Wind Turbines
- Pole-Mounted Turbines: Installed on a freestanding mast, these turbines usually generate more power due to their increased height and exposure.
- Building-Mounted Turbines: Attached directly to a building, they are suitable for urban areas but might produce less energy compared to pole-mounted variants.
Steps Involved in Installing a Small Wind Turbine
- Site Assessment: Conduct a thorough wind site assessment to ensure optimal placement.
- Select Appropriate Equipment: Choose between pole-mounted or building-mounted types based on location and energy needs.
- Legal Permits: Obtain necessary permits and comply with local regulations before installation.
- Foundation Preparation: Establish a strong foundation to ensure stability against high winds.
- Erect the Tower: Assemble and raise the tower carefully, ensuring all components are securely fastened.
- Electrical Connections: Integrate the turbine with your home’s electrical system, possibly requiring professional assistance.
Regular Maintenance Tips for Optimal Performance
Maintaining wind generators is essential for efficient operation:
- Routine Inspections: Regularly check blades, bolts, and electrical connections for wear or damage.
- Lubrication: Ensure moving parts are well-lubricated to reduce friction and prolong lifespan.
- Monitor Performance: Use monitoring systems to track output and detect potential issues early.
By following these guidelines, small-scale wind turbines can provide a reliable source of free electricity while reducing environmental impact.
Step 3: Exploring Hydroelectricity Options for Off-Grid Power Generation
Conducting a Feasibility Study for Micro-Hydro Systems at Home
Generating free electricity through hydroelectric power involves tapping into the continuous flow of water to create energy. Micro-hydro systems are an efficient and sustainable method for producing electricity, especially in rural or off-grid locations. The feasibility of implementing such a system at home relies on a thorough understanding of your local water resources and potential energy output.
How to Conduct a Feasibility Study for Hydroelectricity at Home
Conducting a feasibility study is crucial before investing in a micro-hydro system. This process involves assessing several key factors:
- Water Flow and Head: Start by measuring the flow rate of the water source (in litres per second) and the head, which is the vertical drop (in meters). These two variables determine the potential power output using this formula:
- [ \text{Power (kW)} = \text{Flow rate (L/s)} \times \text{Head (m)} \times 9.81 \times \text{Efficiency} ]
- Efficiency typically ranges from 50% to 70%, depending on the turbine type.
- Site Accessibility: Evaluate how accessible the site is for construction and maintenance activities. Difficult terrain may increase installation costs and complexity.
- Environmental Impact: Consider any ecological impact that the installation might have on local wildlife or plants. Ensure compliance with environmental regulations to avoid legal issues.
- Regulatory Requirements: Check local zoning laws, water rights, and necessary permits. Regulations can vary significantly between regions, so it’s important to consult with local authorities early in the planning process.
Identifying Suitable Water Sources for Hydro Systems
A critical component of harnessing hydroelectric power is identifying an appropriate water source. Here are some tips for evaluating potential sites:
- Permanent Water Flow: Choose a location with a consistent year-round flow. Seasonal variations can significantly affect power reliability.
- Proximity to Power Needs: Ideally, your water source should be close to where you’ll use the electricity, reducing transmission losses and infrastructure costs.
- Natural Gradient: A natural drop or gradient enhances energy generation potential without requiring significant modification to the landscape.
- Quality of Water: Ensure that the water source is free of excessive debris or sediment that could damage equipment over time.
Exploring options like The Water Freedom System can provide valuable insights into achieving water independence, which complements hydroelectric power generation efforts.
Water source energy generation offers an exciting opportunity for those interested in self-sufficiency and sustainable living. With careful planning and evaluation, micro-hydro systems can provide reliable electricity while minimising environmental impact.
This exploration into hydroelectric options paves the way for further sustainable energy solutions, each contributing uniquely to an eco-friendly lifestyle.
Installing DIY Hydroelectric Systems: A Step-by-Step Guide
Harnessing the power of flowing water can be an effective way to generate Free Electricity. Micro-hydro systems convert kinetic energy from water sources into usable electricity, providing a renewable and sustainable energy solution. Here’s how you can set up your own micro-hydro system:
Understanding How Hydroelectric Systems Work
Hydroelectric power systems utilise the flow of water to drive turbines connected to generators. This process transforms the mechanical energy of moving water into electrical energy. With consistent flow, these systems can deliver continuous power, making them a reliable choice for off-grid energy generation.
Requirements for Setting Up a Micro-Hydro System
Before embarking on a DIY micro-hydro setup, consider these site-specific requirements:
- Water Source: A reliable stream or river with sufficient flow and head (vertical drop) is essential.
- Flow Rate: Measure the volume of water passing through the site to determine potential energy output.
- Head: Calculate the vertical distance water falls, influencing the system’s efficiency.
Installation Process for Hydroelectric Systems
1. Site Assessment: Conduct a micro-hydro feasibility study to ensure your location meets all necessary conditions.
2. Acquire Necessary Permits: Check local regulations and obtain permits as hydroelectric installations may affect natural waterways.
3. Select Appropriate Equipment:
- Turbines (e.g., Pelton, Francis)
- Generators
- Control systems
- Piping and wiring
4. Prepare the Site:
- Construct intake channels for water diversion.
- Install pipelines or penstocks to direct water flow efficiently.
5. Install Turbine and Generator:
- Securely mount turbines at specified locations.
- Connect them to generators using appropriate couplings.
6. Electrical Wiring: Ensure proper connection between generators and household electrical systems.
Regulations and Permits
Navigating legal requirements is crucial when installing hydroelectric systems. Regulations vary by region but typically involve environmental assessments and compliance with water use rights. Consult with local authorities to understand specific obligations.
By carefully evaluating water sources and following structured installation steps, you can effectively harness water source energy generation through micro-hydro systems in your home. Additionally, while you’re working on this project, it might be worthwhile to explore other avenues for self-sufficiency such as long-lasting food for survival or even money prayers that could provide additional resources during your transition to a more sustainable lifestyle.
Step 4: Implementing Biomass Energy Solutions as an Alternative Heating Method
Exploring Different Types of Biomass Heating Systems Available
Biomass heating systems are an excellent alternative for those looking to tap into free electricity by using renewable energy sources. These systems use organic materials, like wood, to provide warmth and energy-efficient solutions for your home. Two popular types of biomass heating solutions are pellet stoves and log burners, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Pellet Stoves
Pellet stoves use compressed wood or biomass pellets to generate heat. These units are designed for efficiency and convenience, making them a popular choice among homeowners seeking sustainable energy options.
- Pros:
- High Efficiency: Pellet stoves can achieve up to 90% efficiency, meaning they convert most of the fuel’s energy into usable heat.
- Ease of Use: Automated feeding systems mean that users can load the stove with pellets, set their desired temperature, and let the stove do the rest.
- Consistent Heat Output: Unlike traditional wood-burning stoves, pellet stoves offer a steady heat output without frequent refueling.
- Environmentally Friendly: Pellets are made from compressed sawdust or other waste materials, reducing landfill waste.
- Cons:
- Initial Cost: The upfront cost for pellet stoves is generally higher than that of log burners.
- Dependence on Electricity: Pellet stoves require electricity to power their feeding systems and fans.
- Maintenance: Regular cleaning is necessary to ensure optimal performance and prevent blockages.
Log Burners
Log burners, also known as wood stoves, are a more traditional approach to biomass heating. They burn logs or larger pieces of wood to produce heat.
- Pros:
- Lower Initial Cost: Log burners tend to be less expensive than pellet stoves, making them more accessible for budget-conscious homeowners.
- Independence from Electricity: Unlike pellet stoves, log burners do not rely on electricity, offering peace of mind during power outages.
- Aesthetic Appeal: Many homeowners appreciate the classic look and ambiance that a log burner provides.
- Cons:
- Variable Efficiency: The efficiency of log burners can vary significantly depending on the type of wood used and how well it is seasoned.
- Manual Operation: Operating a log burner requires manual labor—chopping wood, loading the stove, and regulating airflow—to maintain a consistent temperature.
- Smoke Emissions: Log burners can produce smoke emissions if not properly maintained or operated with wet wood.
Comparing Wood Pellets vs Chips
When considering which type of fuel to use in your biomass heating system, it’s important to weigh the differences between wood pellets and chips. Both have unique characteristics that may influence your decision:
- Wood Pellets:
- Made from compacted sawdust or other biomass residues
- Uniform size allows for consistent feeding in automated systems
- Higher energy density compared to chips
- Wood Chips:
- Larger pieces derived directly from chipping wood
- Typically less expensive than pellets
- Require larger storage space due to bulkier form
Choosing between these fuels depends on factors such as availability in your area, budget considerations, and storage capabilities. Each option offers distinct benefits that contribute toward achieving free electricity through eco-friendly means.
Cost Savings Analysis: Switching to Biomass Energy for Heating Needs
Switching to biomass heating systems can lead to significant cost savings compared to traditional electric heating solutions. By utilising wood-fuelled heating solutions, such as wood pellets or chips, you can reduce your reliance on electricity for heating, which often translates into lower energy bills.
Biomass Heating Options
- Wood Pellets: These are made from compressed sawdust and other wood waste materials. They offer high combustion efficiency and a clean burn, making them an economical choice.
- Wood Chips: While less dense than pellets, wood chips are often cheaper and can be sourced locally, adding to their cost-effectiveness.
Comparing Heating Costs
Traditional electric heating systems can be expensive due to fluctuating electricity prices. In contrast, biomass energy offers more stable costs. Here’s a comparison:
- Electric Heating: Typically involves high operational costs due to electricity rates.
- Biomass Energy: Initial setup might be higher, but ongoing costs are generally lower because of the availability and price stability of wood fuels.
Analysing Potential Savings
By switching to biomass energy for your heating needs, you can expect:
- Lower Fuel Costs: The cost per kWh of biomass fuels tends to be lower than electric rates.
- Efficient Energy Use: Biomass systems often operate with higher efficiency compared to electric heaters.
- Long-term Savings: While the initial investment in biomass systems may be significant, long-term savings on fuel costs can outweigh these initial expenses.
Investing in biomass heating options not only contributes to free electricity generation efforts but also offers a financially viable alternative by reducing monthly heating costs. This shift supports a sustainable lifestyle while ensuring consistent heat supply without the financial burden associated with conventional electric systems.
Step 5: Installing Ground Source Heat Pumps as a Sustainable HVAC Solution
Advantages and Considerations When Using Ground Source Heat Pumps in Your Home
Ground source heat pumps, also known as geothermal energy solutions, offer an innovative approach to sustainable heating and cooling. These systems leverage the Earth’s natural thermal energy, providing an efficient and environmentally friendly alternative to traditional HVAC systems.
Advantages of Ground Source Heat Pumps:
- Energy Efficiency: Ground source heat pumps are renowned for their high efficiency. By utilising the constant temperature of the ground, these systems can achieve efficiencies of 300-600%, meaning they produce 3-6 times as much energy as they consume.
- Environmental Impact: Opting for geothermal solutions significantly reduces your carbon footprint. Unlike fossil fuel-based systems, ground source heat pumps emit no greenhouse gases during operation, contributing positively to environmental conservation.
- Cost Savings: Although the initial investment for installing a ground source heat pump can be substantial, the long-term savings on energy bills are noteworthy. With lower operational costs compared to conventional HVAC systems, users often recoup their investment within 5 to 10 years.
- Longevity and Durability: These systems boast a long life span, with underground components lasting up to 50 years and indoor components around 25 years. This durability ensures reliable service over decades.
Evaluating whether a ground source heat pump is right for your home involves considering several factors:
- Initial Investment vs Long-Term Savings: While the upfront cost may seem daunting, it’s crucial to weigh this against potential savings on heating and cooling bills. Many homeowners find that the reduction in energy expenses justifies the initial expenditure over time.
- Property Suitability: Successful installation requires adequate land space for burying loops or pipes. Assessing your property’s geological conditions is also vital since certain soil types and rock formations can affect system efficiency.
- Local Climate Conditions: These pumps perform optimally in moderate climates where there is less extreme demand for heating or cooling. However, they remain viable even in more challenging environments due to their year-round consistency.
- Available Incentives: Many governments provide incentives such as tax credits or rebates to encourage adoption of renewable technologies like geothermal systems. Investigating these opportunities can significantly offset installation costs.
- System Sizing and Design: Proper sizing is essential for maximising efficiency and comfort levels within your home. Consulting with a professional installer ensures that your system meets specific requirements and local regulations.
By incorporating ground source heat pumps into your home’s HVAC system, you not only benefit from free electricity but also take an impactful step towards sustainable living. This technology offers both economic advantages through reduced utility bills and environmental benefits by minimising reliance on non-renewable resources.
Transitioning to this renewable energy solution aligns with broader goals of enhancing self-sufficiency in power generation while making a positive contribution towards global sustainability efforts.
In addition to these sustainable practices, maintaining overall health is equally important. For instance, using products like Metanail Serum Pro can enhance foot health which is crucial when transitioning to more eco-friendly living with ground source heat pumps that often involve more outdoor activities such as gardening or landscaping.
Installing Ground Source Heat Pumps: A Comprehensive Guide
Ground source heat pumps (GSHPs) present an efficient way to harness geothermal energy solutions for heating and cooling your home. These systems utilise the earth’s constant temperature to transfer heat, offering a sustainable alternative to traditional HVAC systems.
How Ground Source Heat Pumps Work
- Heat Extraction: GSHPs circulate a water-based solution through underground pipes, absorbing heat from the ground.
- Heat Transfer: The absorbed heat is transferred to a heat exchanger in your home, which distributes it as needed.
- Cooling Functionality: In warmer months, the process reverses, pulling heat from your home and dissipating it into the ground.
Installation Steps for Ground Source Heat Pumps
- Site AssessmentEvaluate your property for space availability and soil conditions.
- Consider geographical factors that may affect installation.
- System DesignDetermine the appropriate system size based on your home’s heating and cooling requirements.
- Choose between horizontal or vertical piping loops, influenced by land availability.
- Excavation and Loop InstallationHorizontal loops require trenches, while vertical loops involve drilling boreholes.
- Professional equipment is often necessary for this stage.
- Connecting to Home SystemLink the underground loops to the heat pump unit inside your home.
- Ensure compatibility with existing HVAC infrastructure.
- Testing and CommissioningConduct performance tests to ensure optimal functionality.
- Adjust settings as necessary for efficient operation.
Professional vs DIY Installation Options
- Professional Installation:Offers expertise in design and execution.
- Ensures compliance with local regulations and standards.
- Typically results in faster completion times.
- DIY Installation:Potentially reduces upfront costs if you possess technical skills.
- Requires careful research and adherence to legal guidelines.
- Risk of increased long-term maintenance if improperly installed.
Selecting the right approach depends on your budget, technical acumen, and time considerations. Proper installation of GSHPs not only enhances their efficiency but also capitalises on the advantages of ground source heat pumps as a viable step towards achieving Free Electricity.
In addition to energy efficiency, exploring day trading can be a profitable venture if you’re looking to invest in renewable energy stocks or related sectors. Meanwhile, maintaining a healthy lifestyle while managing such investments is crucial; hence understanding how to have healthy blood sugar could be beneficial. Furthermore, if you’re experiencing stress due to financial uncertainties or personal issues like heartache when your soulmate moves on, seeking professional help or guidance can provide relief. Lastly, if you’re facing challenges in your personal life such as low libido which could affect your overall well-being, exploring methods suggested in this guide on reviving libido may offer some helpful insights.
Conclusion: Embracing Renewable Energy Sources for Free Electricity Generation at Home
Generating free electricity at home is no longer a distant dream but an achievable reality. By tapping into renewable energy sources like solar, wind, hydroelectricity, biomass, and ground source heat pumps, you can significantly reduce your dependence on traditional power grids. These methods not only cut down on your electricity bills but also play a crucial role in promoting environmental sustainability.
Exploring these options empowers you to take control of your energy needs. Whether you’re considering the installation of solar panels or evaluating the feasibility of a micro-hydro system, each step brings you closer to self-sufficiency. For those who seek an all-encompassing solution, The Ultimate OFF-GRID Generator offers a comprehensive approach to achieving energy independence.
If you’re interested in learning more about how to generate your own electricity at home for under $100, this guide provides practical insights and steps to follow.
Embrace the possibilities of renewable energy and embark on the journey towards sustainable living. Each decision you make contributes to a greener future and enhances your home’s resilience against fluctuating energy markets. Consider incorporating these innovative solutions into your lifestyle and witness the transformation as you generate your own power effortlessly.

Leave a Reply